Functional additives in the ceramic industry
Ceramic surfactants
Surfactants play a key role in controlling the viscosity of ceramic suspensions, optimizing the flowability of slip and glazes. Depending on their formulation and specific function, they can act as deflocculants, stabilizers or dispersants, adapting to different stages of the process.
We can classify them according to their rheological function:
- Viscosity reducers
They aremainly used in slips and glazes to reduce internal friction between particles, which facilitates pumping, bell or curtain glazing and improves performance in automatic application processes. This improved fluidity allows working with higher solids without compromising suspension stability.
- Viscosity enhancers
They act in opposite but complementary ways. In formulations where it is necessary to avoid sedimentation (such as in resting tanks or dense glazes), these additives increase viscosity in a controlled manner, stabilizing the mixture and guaranteeing a uniform application.
- Dispersing agents for non-aqueous ceramic inks
In digital ceramic printing, where solvent systems are used, additives are required to ensure fine dispersion of the pigments without affecting the surface tension of the ink. The right choice of surfactant directly influences the accuracy of the printed design, adhesion and abrasion resistance after glazing.
Anti-slip treatments
The need for safe surfaces in wet or high traffic areas has driven the development of anti-slip treatments compatible with contemporary ceramic finishes.
- Increased coefficient of friction
By means of microtexturization or additives that modify the surface tension of the enamel, greater slip resistance is achieved without modifying the visual appearance of the final product.
- Formulation adapted to each system
These treatments are designed to be integrated into both industrial processes (in-line glazing) and in-situ applications (final work), allowing versatility without compromising durability.
- Compatibility with different formulations
Its effectiveness has been validated on matte, glossy or satin finishes, and its application does not interfere with other surface treatments such as water repellents or hardeners.
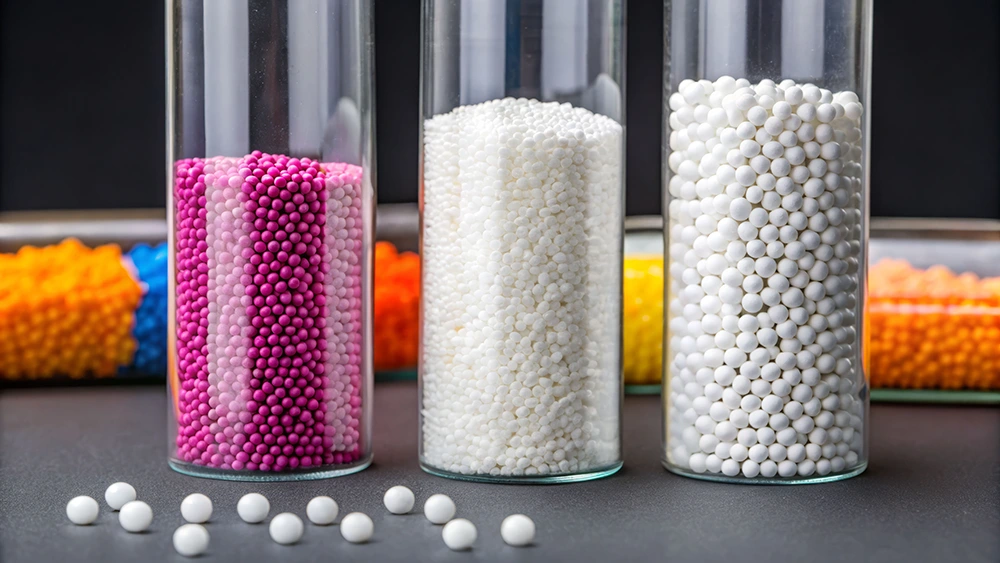
High density alumina balls
Efficient grinding of hard raw materials such as quartz, feldspar or kaolin is essential to achieve an optimum particle size for good compaction and sintering.
- High density alumina balls
With a hardness greater than 9 on the Mohs scale, these balls offer exceptional wear resistance, minimizing contamination of the ground product and extending mill life.
- High energy efficiency
Thanks to their density and sphericity, they transfer kinetic energy better, allowing for greater size reduction in less time and with lower energy consumption.
- Adaptability to the process
Available in a wide range of diameters, these balls allow to fine tune the process according to the type of mill and the type of slurry or paste to be processed.